Hurricane season is a period when the formation of tropical cyclones, including hurricanes, is most likely to occur. While the exact dates vary based on geographic location, these seasons typically coincide with the warmest months of the year. During this time, coastal regions and areas susceptible to tropical storms brace themselves for potential severe weather.
What Causes Hurricane Season?
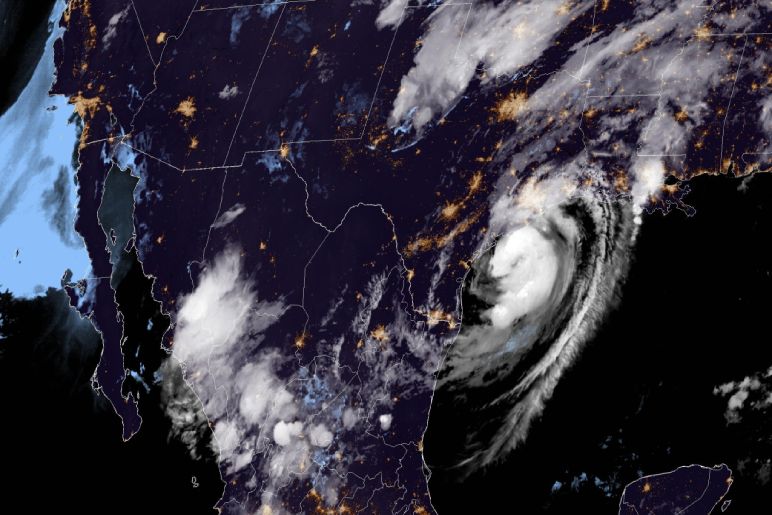
Hurricanes are complex meteorological phenomena that require a specific set of conditions to form. Warm ocean waters act as the primary energy source for these storms. As the ocean temperature rises, the atmosphere above becomes increasingly unstable. This instability, combined with other factors such as low wind shear and a pre-existing disturbance, can lead to the development of a tropical depression.
A tropical depression is a system of organized clouds and thunderstorms with a closed circulation and maximum sustained winds of up to 38 miles per hour (33 knots). If the system intensifies and sustained winds reach 39-73 mph (34-63 knots), it becomes a tropical storm and is assigned a name. When sustained winds exceed 74 mph (64 knots), the storm is classified as a hurricane.
Hurricane Season by Region

The timing of hurricane season varies across different regions:
- Atlantic Hurricane Season: Typically runs from June 1st to November 30th. This basin includes the Caribbean Sea, Gulf of Mexico, and the Atlantic Ocean.
- Eastern Pacific Hurricane Season: Generally extends from May 15th to November 30th. This basin covers the Pacific Ocean off the west coast of Mexico and Central America.
- Central Pacific Hurricane Season: Occurs from June 1st to November 30th. This basin encompasses the Pacific Ocean north of the equator and west of 140 degrees west longitude.
It’s crucial to remember that these are general guidelines, and the actual activity within each season can vary significantly from year to year. Some years may witness an unusually high number of storms, while others may be relatively quiet.
Impact of Hurricanes
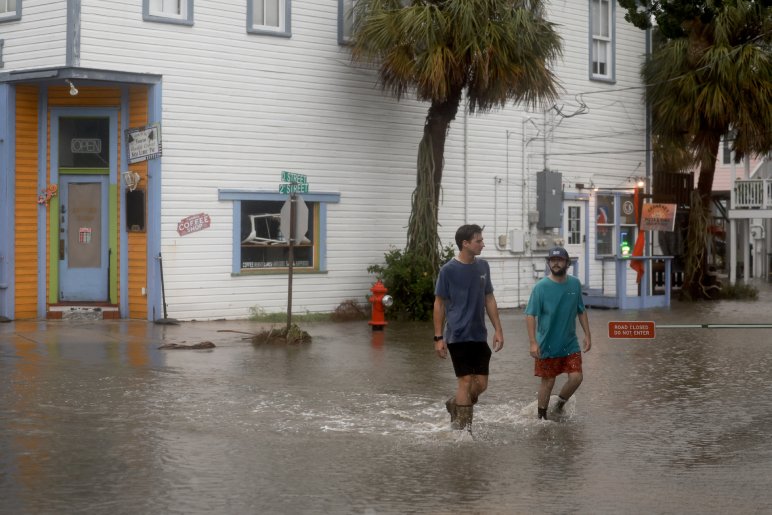

Hurricanes, nature’s most formidable storms, unleash catastrophic consequences when they make landfall. These colossal weather systems bring a destructive force that can reshape landscapes, disrupt lives, and cause immense economic loss. Let’s delve into the far-reaching impacts of hurricanes.
Physical Destruction
- Wind Damage: Hurricane-force winds can cause widespread destruction, uprooting trees, damaging buildings, and shattering windows.
- Storm Surge: The abrupt rise in sea level caused by a hurricane can inundate coastal areas, leading to catastrophic flooding, erosion, and property damage.
- Rainfall and Flooding: Intense rainfall associated with hurricanes can trigger inland flooding, landslides, and mudslides, causing significant damage to infrastructure and homes.
Economic Consequences
- Property Loss: Hurricanes inflict substantial property damage, including homes, businesses, and public infrastructure.
- Business Disruption: The closure of businesses due to hurricane-related damage and power outages can lead to economic losses and job displacement.
- Insurance Claims: The aftermath of a hurricane often results in a surge of insurance claims, straining the insurance industry.
- Tourism Impact: Hurricanes can deter tourists from visiting affected areas, impacting the local economy.
Environmental Impact

- Coastal Erosion: Storm surge and high waves can accelerate coastal erosion, leading to beach loss and damage to coastal ecosystems.
- Water Pollution: Hurricanes can cause contamination of water supplies due to flooding and sewage overflows.
- Wildlife Disruption: Hurricanes can disrupt wildlife habitats, leading to population declines and changes in ecosystems.
Human Impact
- Loss of Life: Hurricanes tragically claim lives due to drowning, injuries, and structural collapses.
- Displacement: Hurricanes force people to evacuate their homes, leading to temporary or permanent displacement.
- Psychological Trauma: The experience of a hurricane can have long-lasting psychological effects on survivors.
- Infrastructure Damage: Hurricanes can damage critical infrastructure, including roads, bridges, power lines, and communication systems, hindering recovery efforts.
The Science Behind Hurricanes
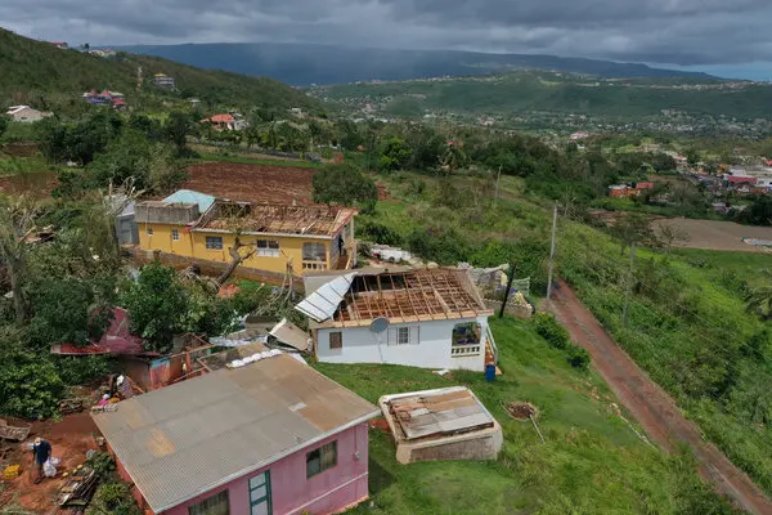

Hurricanes are complex meteorological phenomena that require a specific set of conditions to form and intensify. Warm ocean waters act as the primary energy source for these storms. As water temperatures rise, evaporation increases, creating a humid atmosphere. This moisture-laden air rises, cools, and condenses into clouds, releasing heat energy in the process. This heat energy further fuels the storm, creating a cycle of intensification.
A low-pressure system is also essential for hurricane formation. As air converges towards the low-pressure center, it begins to rotate due to the Earth’s rotation (Coriolis effect). This rotation intensifies as the storm gains strength.
Preparing for Hurricane Season
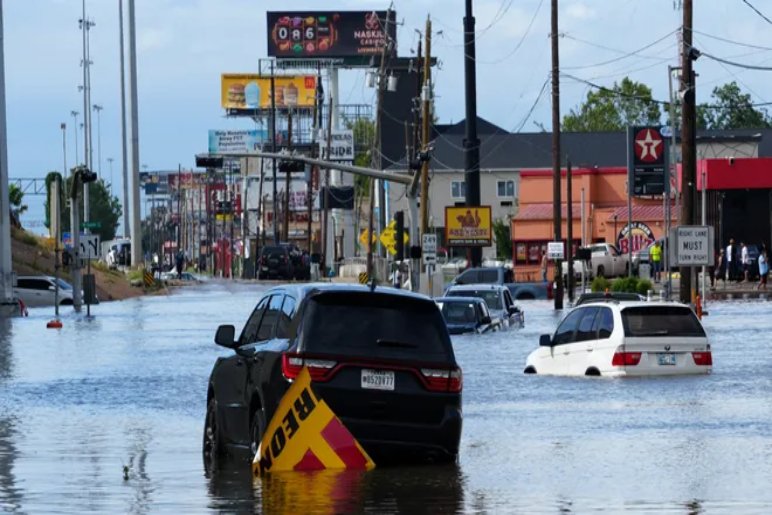

Hurricane season is a time of heightened vigilance for many coastal residents. With powerful winds, torrential rain, and the threat of storm surge, hurricanes can cause significant damage and disruption. But with proper preparation, you can significantly reduce your risk and protect yourself and your loved ones.
Understanding Your Risk
The first step in hurricane preparedness is understanding your risk. If you live in a hurricane-prone area, it’s essential to know your evacuation zone, the potential for flooding, and the strength of your home’s structure. This information will help you make informed decisions about your preparedness plan.
Building an Emergency Kit
A well-stocked emergency kit is crucial for surviving a hurricane. Include essential supplies such as:
- Water: At least a gallon of water per person, per day for several days.
- Food: Non-perishable items like canned goods, energy bars, and dried fruit.
- First aid kit: Including bandages, antiseptic, pain relievers, and any necessary medications.
- Flashlights and batteries: For lighting when the power goes out.
- Battery-powered radio: To stay informed about weather updates.
- Important documents: Copies of insurance policies, identification, and medical records.
Securing Your Home
Protecting your home from hurricane damage is essential. Take the following steps:
- Trim trees: Remove weak or dead branches that could become projectiles.
- Secure outdoor objects: Bring in or securely fasten any loose items like lawn furniture, grills, and garbage cans.
- Protect windows: Install hurricane shutters or board up windows with plywood.
- Review insurance coverage: Ensure you have adequate homeowners insurance with appropriate coverage for wind and flood damage.
Hurricane Mitigation and Recovery
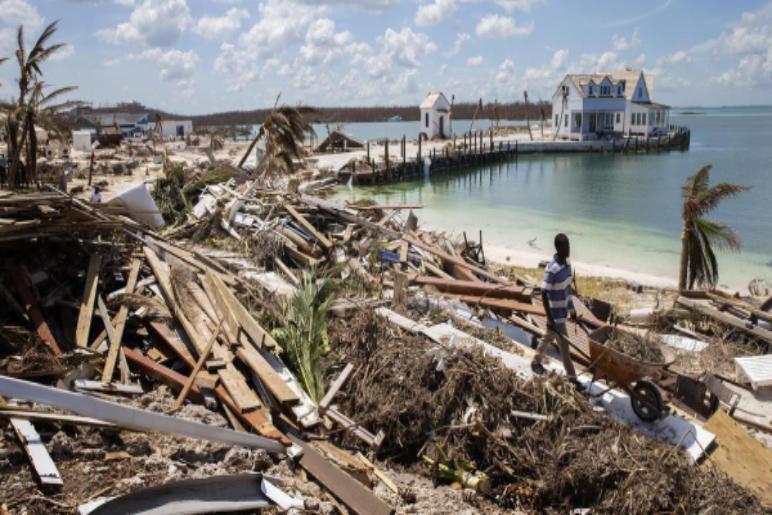

While preparation is crucial, it’s also essential to understand hurricane mitigation and recovery strategies. Building codes and construction practices can be designed to withstand hurricane forces. Investing in flood insurance can provide financial protection against storm surge and flooding.
In the aftermath of a hurricane, communities face the daunting task of recovery. This process involves clearing debris, restoring power and communication lines, and providing essential services to affected residents. Government agencies, non-profit organizations, and volunteers play a vital role in supporting recovery efforts.
By understanding the nature of hurricanes, taking proactive steps to prepare, and supporting mitigation and recovery initiatives, we can enhance our resilience to these powerful storms and minimize their impact on our communities.
Climate Change and Hurricanes
Climate change is expected to intensify the impacts of hurricanes. Rising sea levels increase the risk of storm surge, while warmer ocean temperatures provide more energy for storms to develop. Changes in precipitation patterns can also contribute to more intense rainfall events. As a result, coastal communities face growing challenges in adapting to a changing climate and preparing for more severe hurricane seasons.
Conclusion
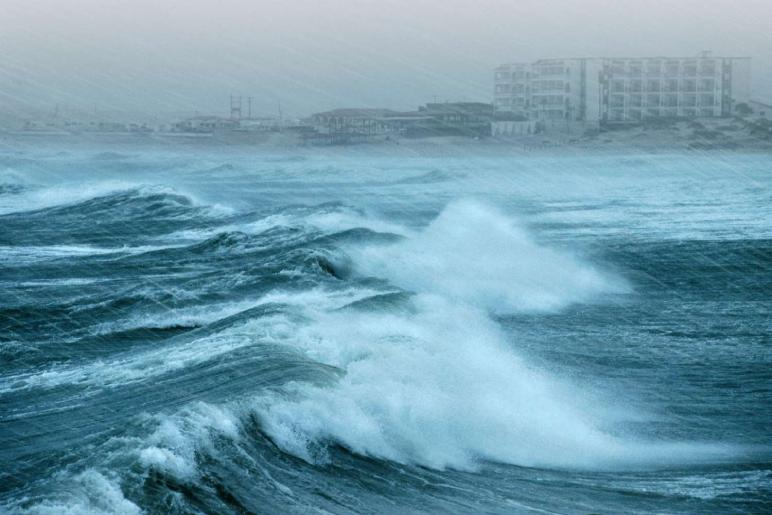

Hurricane season is a time of heightened awareness and preparation for coastal communities. While these storms can be destructive, understanding the risks, taking proactive measures, and staying informed can significantly mitigate their impact. By building an emergency kit, securing your home, and having a well-practiced evacuation plan, you can increase your chances of staying safe during hurricane season. Remember, early preparation is key.
Stay informed about weather forecasts, heed warnings from local authorities, and prioritize the safety of yourself and your loved ones. With proper planning and resilience, you can weather the storm.
Read More:
- Motion of the Ocean: Introduction to Wave Energy
- Managing Your Green Lifestyle: Practical Tips for a Sustainable You
- 5 Ways to Give Your Old Smartphone a New Life: Responsible Recycling Options
Featured Image Source: https://tinyurl.com/3fshr5m4

